Neutron Stars and Pulsars – Mathematical Differences
Mathematical Difference: Neutron Star vs Pulsar
Neutron Star
A neutron star is a highly dense remnant of a massive star after a supernova explosion. It is characterized by:
- Mass:
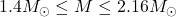
- Radius:
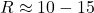 km
km - Density:
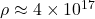 kg/m³
kg/m³ - Escape velocity:
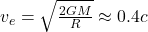
Pulsar
A pulsar is a type of neutron star that emits periodic electromagnetic radiation due to its rapid rotation and strong magnetic field. It follows additional mathematical constraints:
- Rotation period:
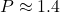 ms to a few seconds
ms to a few seconds - Magnetic field strength:
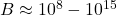 Gauss
Gauss - Spin-down rate:
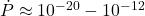 s/s
s/s - Energy loss due to dipole radiation:
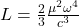
Key Difference
All pulsars are neutron stars, but not all neutron stars are pulsars. A neutron star becomes a pulsar if:
- It has a strong enough magnetic field (
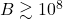 Gauss).
Gauss). - It rotates rapidly enough to emit detectable periodic signals.
Over time, pulsars lose energy and slow down, eventually becoming regular neutron stars.